An integrated approach to iron salt use in urban water systems
Drinking water supply and wastewater services are essential components of an urban water system. However, in most cases they are operated separately, often by different entities. By recognising and optimising their connections through a system-wide approach, an integrated management strategy delivers tremendous economic, environmental and social benefits.
The team was awarded an ARC Linkage project (LP140100386) to carry out a world-first investigation of integrated urban water management through multiple and beneficial use of iron salts. Through thorough evaluation and optimisation, the MulFe strategy was shown to achieve at least cost, higher quality wastewater effluent, biogas, and sewage sludge, in combination with maintaining high quality drinking water.

Collaborators
- Urban Utilities
- DCwater is life
- Water Research Australia
- SEQ Water
- PUB
Project Outcomes
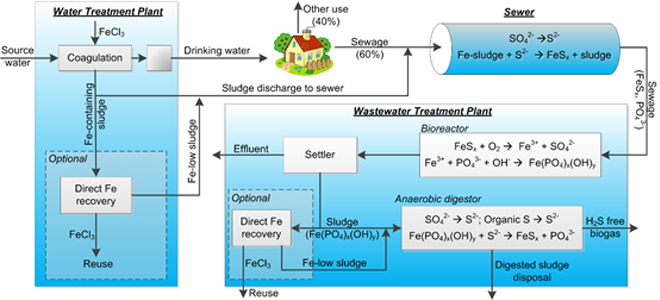
The MulFe project developed and demonstrated an integrated and innovative strategy, and the associated science and technologies, to achieve multiple beneficial uses of iron salts in the urban water system. Iron chloride (FeCl3) was used in place of alum, the most common coagulant in drinking water treatment. Normally, spent coagulant from drinking water treatment is considered a waste product. However, for the MulFe strategy, the iron-containing spent coagulant is then further used for corrosion and odour control by dosing into sewers. Further downstream, this iron also contributes to phosphorus removal in wastewater treatment reactors, and hydrogen sulfide removal from biogas in anaerobic digesters. The strategy thus substantially reduces the use of chemicals in the entire urban water system, and improves the sustainability of water utility services. The MulFe project is an exemplar for integrated urban water management.
The project was awarded the Australian Water Association Research Innovation Award, Queensland in 2019.
Media:

Publications
- Rebosura, M., S Salehin, I Pikaar, X Sun, J Keller, K Sharma, Z Yuan. 2018. A comprehensive laboratory assessment of the effects of sewer-dosed iron salts on wastewater treatment processes. Water Research 146:109-117.
- Shrestha, S, K Sharma, Z Chen, Z Yuan. 2019. Unravelling the influences of sewer-dosed iron salts on activated sludge properties with implications on settleability, dewaterability and sludge rheology. Water Research, Volume 167, 15 December 2019, 115089.
- Kulandaivelu, J., Gao, J., Song, Y., Shrestha, S., Li, X., Li, J., Doederer, K., Keller, J., Yuan, Z., Mueller, J.F. and Jiang, G. (2019) Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs from Wastewater Due to Ferric Dosing in Sewers. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(11):6245-6254
- Sirajus Salehin, Jagadeeshkumar Kulandaivelu, Mario Rebosura Jr., Wakib Khan, Reece Wong, Guangming Jiang, Peter Smith, Paul McPhee, Chris Howard, Keshab Sharma, Jürg Keller, Bogdan C. Donose, Zhiguo Yuan, and Ilje Pikaar 2019. Opportunities for reducing coagulants usage in urban water management: the Oxley Creek Sewage Collection and Treatment System as an example. Water Research, Volume 165, 15 November 2019, 114996.
- Jagadeeshkumar Kulandaivelu, Sohan Shrestha, Wakib Khan, Jason Dwyer, Alan Steward, Leo Bell, Paul McPhee, Peter Smith, Shihu Hu, Zhiguo Yuan, Guangming Jiang. 2020. Full-scale investigation of ferrous dosing in sewers and a wastewater treatment plant for multiple benefits. Chemosphere, 250: 126221.
- Mario Rebosura Jr., Sirajus Salehin, Ilje Pikaar, Jagadeeshkumar Kulandaivelu, Guangming Jiang, Jürg Keller, Keshab Sharma, Zhiguo Yuan. 2019 Effects of in-sewer dosing of iron-rich drinking water sludge on wastewater collection and treatment systems. Water Research, Volume 171, 15 March 2020, 115396.
- Mario Rebosura, Sirajus Salehin, Ilje Pikaar, Jürg Keller, Keshab Sharma, Zhiguo Yuan. 2021. The impact of primary sedimentation on the use of iron-rich drinking water sludge on the urban wastewater system. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 402:124051.
- Shrestha, S, J Kulandaivelu, K Sharma, G Jiang, Z Yuan. 2019. Effects of dosing iron- and alum-containing waterworks sludge on sulfide and phosphate removal in a pilot sewer. Chemical Engineering Journal, 386: 124073.
- Sirajus Salehin, Jagadeeshkumar Kulandaivelu, Mario Rebosura Jr., Olaf van der Kolk, Jurg Keller, Katrin Doederer, Wolfgang Gernjak, Bogdan C. Donose, Zhiguo Yuan and Ilje Pikaar. 2020. Effects of aging of ferric-based drinking water sludge on its reactivity for sulfide and phosphate removal. Water Research, 184: 116179.
- Sirajus Salehin, Mario Rebosura Jr., Jurg Keller, Wolfgang Gernjak, Bogdan C Donose, Zhiguo Yuan and Ilje Pikaar. Recovery of in-sewer dosed iron from digested sludge at downstream treatment plants and its reuse potential. Water Research, online 14 February 2020, 115627.
- Sirajus Salehin, Jagadeeshkumar Kulandaivelu, Mario Rebosura Jr., Olaf van der Kolk, Jurg Keller, Katrin Doederer, Wolfgang Gernjak, Bogdan C. Donose, Zhiguo Yuan and Ilje Pikaar. 2020. Effects of aging of ferric-based drinking water sludge on its reactivity for sulfide and phosphate removal. Water Research, 184: 116179.
- Sirajus Salehin, Mario Rebosura Jr., Jurg Keller, Wolfgang Gernjak, Bogdan C Donose, Zhiguo Yuan and Ilje Pikaar. Recovery of in-sewer dosed iron from digested sludge at downstream treatment plants and its reuse potential. Water Research, online 14 February 2020, 115627.
- Gutierrez, O., Park, D., Sharma, K.R. and Yuan, Z. (2010) Iron salts dosage for sulfide control in sewers induces chemical phosphorus removal during wastewater treatment. Water Research 44(11), 3467-3475.
- Ge, H., Zhang, L., Batstone, D., Keller, J. and Yuan, Z. (2012) Impact of Iron Salt Dosage to Sewers on Downstream Anaerobic Sludge Digesters: Sulfide Control and Methane Production. Journal of Environmental Engineering 139(4), 594-601.
- Pikaar, I., Sharma, K., Hu, S., Gernjak, W., Keller, J. and Yuan, Z. (2014) Reducing sewer corrosion through integrated urban water management. Science 345(6198), 812-814.
- Sun, J., Pikaar, I., Sharma, K.R., Keller, J. and Yuan, Z. (2015) Feasibility of sulfide control in sewers by reuse of iron rich drinking water treatment sludge. Water Research 71, 150-159.
Project members
Other members
- Ilje Pikaar
- Sirajus Salehin
- Jagadeeshkumar Kulandaivelu
- Sohan Shrestha


